
Lihat Daftar Isi
Coolant solution refers to the steps or measures required to address various issues that arise in coolant applications (coolant problems) in the field. Below is a list of the mentioned coolant problems along with their solutions.
1. Chip Issues
- Chips are waste in the form of small metal fragments produced from metalworking processes on CNC machines
- Problems
- Obstructing coolant flow
- Clogging filters
- Breeding ground for bacteria
- Damaging the finish
- Increasing conductivity leading to corrosion
- Solutions
- Coolant filtration
- Centrifugation/magnet
- Settling
2. Bacterial Issues
- Bacteria usually reside at the bottom of the tank, stagnant areas, chips, and waste.
- They thrive on minerals in water, tramp oil, coolant concentrate, and food residues.
- Problems
- Odor, rust
- Solutions
- Ensure proper preparation of the coolant solution (add water to the container first, then coolant)
- Use pure water
- Daily coolant top-up
- Concentration control
- Tramp oil control
- Prevent lubricant contamination
- Maintain machine cleanliness
- Complete cleaning (once a year)
3. Fungal Issues
- Fungi grow on the surface of the coolant tank.
- Tend to grow in synthetic coolants.
- Problems
- Clogging, odor
- Solutions
- Maintain machine cleanliness
- Physical handling
- Fungicide
- Healthy bacterial population
- Use DI water
Read more: Bacterial and Fungal Problems in Metalworking Fluids
4. Eczema Issues
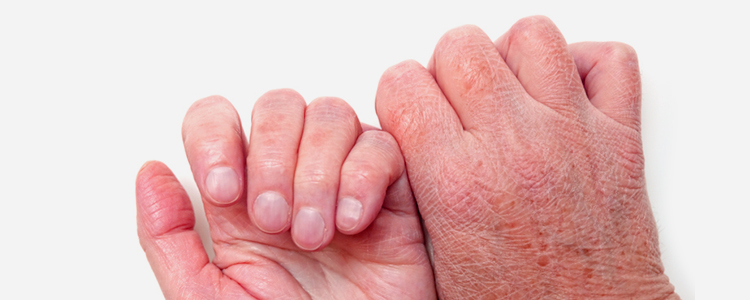
- Eczema, also known as dermatitis, causes itchy skin.
- Causes: extreme pH, solvents, dissolved metals, tramp oil, straight oil, protective cream, dirty coolant, biocide
- Problems
- Itchy skin, health disturbances
- Solutions
- Avoid direct contact with coolant
- Avoid using protective cream
- Relocate allergic operators
- Maintain optimal coolant concentration
- Use microbiocide correctly
- Use proper PPE and tools
5. Tramp Oil Issues

- Tramp oil: machine oil that leaks and mixes with coolant
- Problems
- Bacterial growth
- Reduced tool life
- Filtration obstruction
- Smoke, oil mist, sticky residue
- Solutions
- Address oil leaks
- Use scrounger belts to remove tramp oil
- Purify coolant through other methods
- If severe: replace with new coolant
Read more: Tramp Oil: The Causes, Problems, and Solutions
6. Seal Issues
- Seals continuously exposed to coolant can swell.
- Seal durability depends on: seal material, coolant type, workload, installation method.
- Problems
- Seals swelling and getting damages
- Solutions
- Use Viton seals (stronger)
- Use good quality coolant, consult with Eonchemicals
7. Residue Issues
- Types of residues: thin, soft, hard, sticky, and crystalline
- Problems
- Can interfere with: dial calipers, gauges, auto tool changers, position sensing scales, precision grinders, cutting tool inserts, transfer line pallets
- Solutions: Use good/appropriate coolant; consult with us
8. Foam Issues
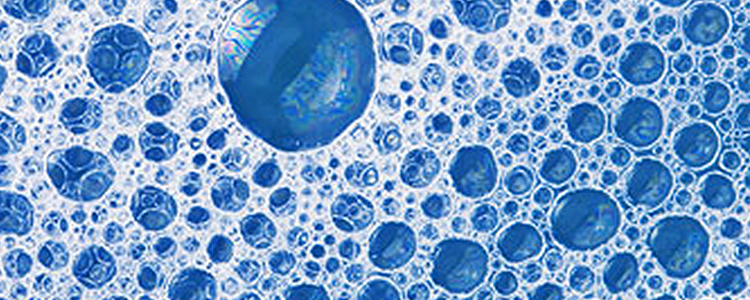
- Foam occurs due to the presence of gas, liquid, and agitation.
- Triggers: air leaks (packing, joints), cascading, cavitation, low coolant level, coolant type, etc.
- Problems:
- Dirty floors
- Safety hazards
- Wasteful
- Disrupts cooling and lubrication processes
- Solutions:
- Address physical causes with physical actions
- Address chemical causes with antifoam chemicals
Read more: Foaming on Metalworking Fluids and The Solutions
9. Paint Issues
- Regular paint (alkyd type) is generally not resistant to coolant.
- Problems
- Paint peeling and disrupting the system
- Solutions
- Use epoxy or polyurethane paint
10. Rust Issues

- Rust can occur due to low pH, parts sticking together, bacteria, contamination, improper grounding.
- Problems
- Machine damage
- Unusable parts
- Solutions
- Use DI water
- Maintain optimal concentration
- Use rust preventive
- Control bacteria
- Check water content (if using neat oil)
- Ensure proper grounding
- Prevent coolant contamination
- Use coated plastic or cardboard to separate parts
- Avoid contact between different metals
11. Excessive Usage Issues
- PCauses of excessive usage:
- Weak concentration control
- Use of hard water
- Long intervals between top-ups
- Low-grade coolant
- Leaks
- Poor technical service
- Problems: increased costs
- Solutions: identify the cause and apply the appropriate coolant solution
Summary
- Problems in coolant applications: Chips, bacteria, fungi, eczema, tramp oil, seals, residues, foam, paint, rust, excessive usage.
- All the above problems lead to losses (quality degradation, damage, wastage).
- All problems can be addressed by identifying and eliminating the causes.
- The most common preventive measures are: using DI water and maintaining coolant concentration.
For more information on coolant solutions or coolant/metalworking fluid products, please contact us.
Consult with EON Now
We are ready to listen and provide the right chemical solution for you. Consultation with our experts is free!
 Home
Home